BLOG
Review: Acupuncture therapy is an effective treatment for patients with fibromyalgia
Zhang, X. C., Chen, H., Xu, W. T., Song, Y. Y., Gu, Y. H., & Ni, G. X. (2019). Acupuncture therapy for fibromyalgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of pain research, 12, 527–542.
https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S186227
QUESTION
Is acupuncture therapy an effective treatment for patients with fibromyalgia?
DATA SOURCES
Studies were identified by searching PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Embase, the China National Knowledge Infrastructure, the Chinese Science and Technology Periodical Database, and the Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (up to May 2018); manual searches of reviews related to fibromyalgia treatments.
STUDY SELECTION
Studies were selected if they were randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared an acupuncture group with a sham or conventional medication group. 12 RCTs met the selection criteria (Fig 1).
DATA EXTRACTION
One author performed searches. Two authors screened eligible studies, then independently extracted and evaluated data. Risk of bias was assessed according to the Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool. Quality of evidence was evaluated using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) Guideline Development Tool. Statistical analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software.
MAIN RESULTS
Meta-analysis showed that acupuncture was significantly more effective than sham acupuncture in reducing pain and improving the quality of life in both short and long terms. Acupuncture was significantly more effective than conventional medication in reducing pain in both short and long terms. There were no serious adverse events found during acupuncture.
CONCLUSION
Acupuncture therapy is an effective treatment for patients with fibromyalgia.
COMMENTARY
Authors identified 12 RCTs that address the question. Sample size ranged from 20 to 164 (Table 1). Interventions in the treatment group were acupuncture and electroacupuncture. The interventions in the control group were sham acupuncture, sham electroacupuncture, and conventional medication.
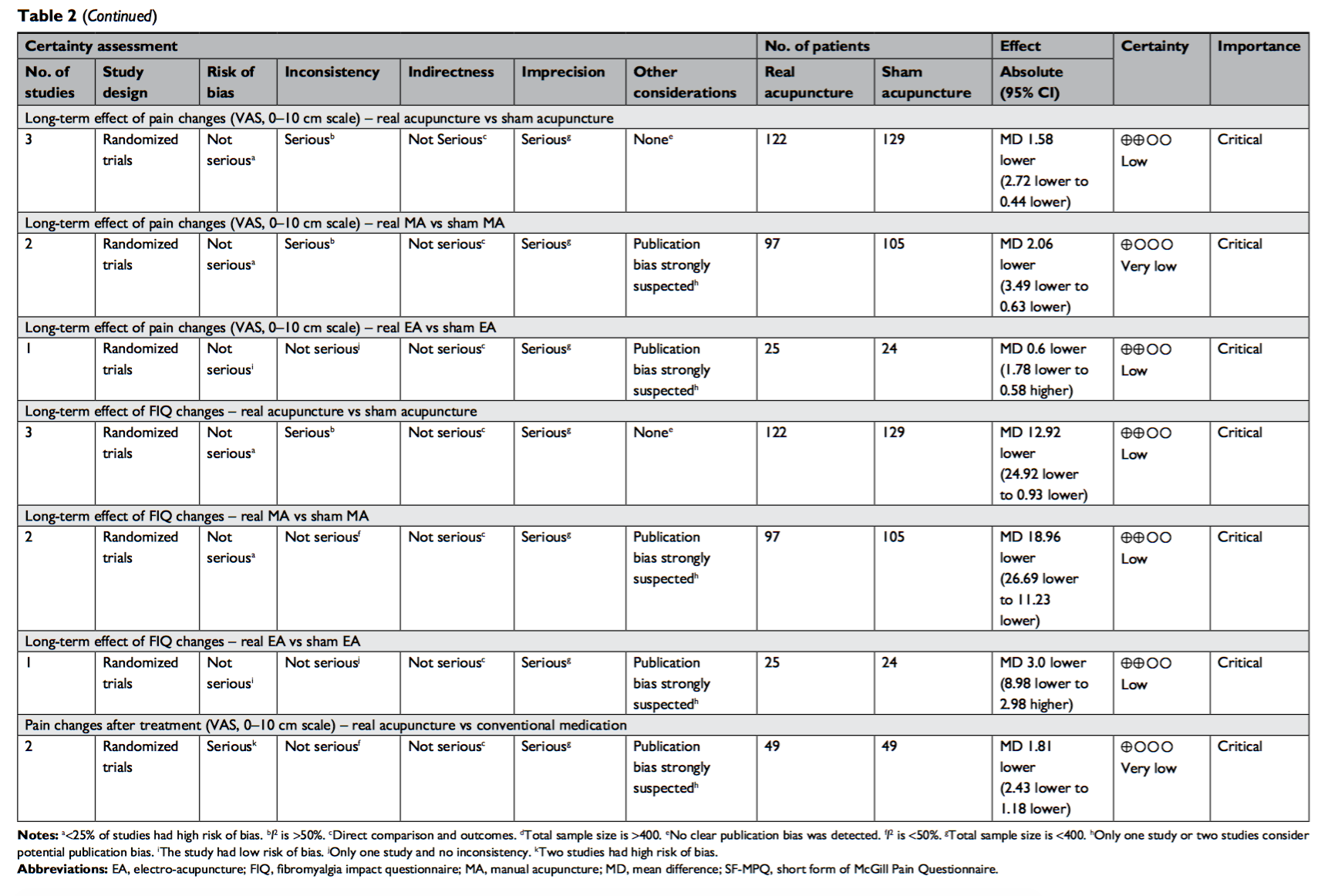
Although there was high performance bias, most of the studies were rated as low risks of bias. According to the GRADE system, most of the studies were classified as moderate to low quality while 1 study (long-term effect of VAS changes in acupuncture vs sham) and 2 studies (VAS changes after treatment in acupuncture vs conventional medication) were classified as very low quality (Table 2).
The result of the 9 studies showed that acupuncture was significantly better in reducing pain in terms of VAS (Fig A). The subgroup analysis showed that both acupuncture and electroacupuncture were significantly better than sham groups.
The result of the 2 studies showed that acupuncture and sham acupuncture were not significantly different in reducing pain in terms of SF-MPQ (Fig B).
The result of the 4 studies showed that acupuncture was significantly better in improving quality of life in terms of FIQ (Fig C). The subgroup analysis showed that acupuncture was significantly better than sham acupuncture while electroacupuncture was not significantly different from sham electroacupuncture.
The result of the 3 studies showed that acupuncture was significantly better in terms of long-term effect of VAS changes (Fig D). The subgroup analysis showed that acupuncture was significantly better than sham acupuncture while electroacupuncture was not significantly different from sham electroacupuncture.
The result of the 3 studies showed that acupuncture was significantly better in terms of long-term effect of FIQ changes (Fig E). The subgroup analysis showed that acupuncture was significantly better than sham acupuncture while electroacupuncture was not significantly different from sham electroacupuncture.
Total of 3 studies compared acupuncture therapy with conventional medication. The result of the 2 studies showed that acupuncture was significantly better in reducing pain in terms of VAS (Fig 4A). The result of the 1 study showed that acupuncture was significantly better in terms of long-term effect of VAS changes (Fig 4B).
Authors conclude that “acupuncture therapy is an effective and safe treatment for patients with FM [fibromyalgia], and it can be recommended for the management of FM. However, more large-sample RCTs are needed to investigate the therapeutic effect of EA [electroacupuncture] for FM in the long term.”